Beef Cattle Facilities Feet Beef Cattle Facilities Rooming
Introduction
In New England, beef enterprises are cow/dogie, feeder, or a combination of both. Cow/calf enterprises usually require less fiscal investment in facilities than feeder operations. Feeder cattle facilities crave more confinement pens, more than automation of feeding systems and less demand for roofed shelters. Each type of facility must be designed appropriately.
Several different designs for housing and treatment facilities are suitable for beefiness operations taking into consideration the weather, topography, and the availability of feed and pasture. It is important to know all the rules and regulations with respect to location, design, and blazon of functioning. Check with your local Edifice Inspector to obtain the required permits prior to edifice or renovating your existing facility. You lot should likewise talk to an experienced architect or contractor to ensure the cost of the facility is within the objectives of the functioning.
It is of import to choose a location for buildings and treatment facilities that is on well-drained soil with properly designed surface water drainage situated abroad from streams, other bodies of water and is not close to population centers. Bank check with your county Natural Resource and Conservation Service (NRCS) office for recommended guidelines.
Some Recommended Structures for Beef Cattle Housing
Open sided, single slope roof shed

This type of housing is most typical of structures used and is suitable for all cattle on the subcontract. This is the least expensive of new structures and very like shooting fish in a barrel to build. Open sheds should face the south for winter sunday and block the prevailing winds. Pole barns of this design tin be partitioned for groups of animals without complicated interior structure.
Open up sided, clear span pole shed

The articulate bridge provides more space for equipment to remove manure and thus any side of the edifice can be open up to the surroundings. The gable finish of the befouled is recommended to be open up then that the belch of rain and snow is not over the open side of the building. When the gable end is open, the trophy areas are unremarkably deeper and provide more protection from the wind. The back end of the structure may be nighttime and damp and may need additional design attention for ventilation and lighting. This blazon of housing is more applied for smaller sized herds (under 20 head of cattle).
Former Dairy Barns

Today at that place are many unused dairy barns due to dairy farmers either retiring or dispersing. The renovation costs are usually less than the price of a new structure. Lighting and ventilation are ordinarily acceptable in former dairy facilities for employ by beef cattle. Manure removal is a major piece of the renovation programme. Conventional necktie stalls that are used on New England dairy farms with a gutter are not recommended. Free stall barns are the ideal dairy facility for utilize with beef cattle since the manure handling is already set-upwardly.
Hoop Barns

One of the least expensive structures for housing cattle is the hoop befouled. Hoop barns are similar to greenhouses. One disadvantage is the heat and ventilation problems during the summer months, but this should not pose an event if you are planning on grazing your cattle during the warmer climate months.
Feeding Equipment
Feed Bunks
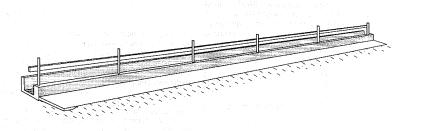
The chief requirements for feed bunks are that they are practical, skilful quality, rugged, and economical. The bunk length and chapters should meet livestock requirements.
Portable Hay Feeders
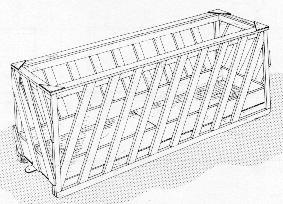
This portable feeder is a proven hay-saving design for free-choice supplementary hay feeding in a field, feedlot, or loose housing barn. The sloping spacers allow cattle of varying sizes to feed comfortably with their heads inside the feeder. This helps to reduce waste product since cattle do non take to withdraw their heads to stand and chew.
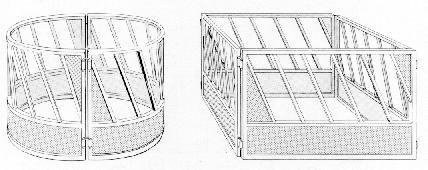
Round and big bale feed racks are easy to load, movement, and also preclude hay wastage. The round version requires a bender to reform the foursquare tube runway, but the round shape makes it easier to ringlet it from place to place. The square version is easier to build in the farm shop, and it tin can be completely collapsed for transport in a pickup truck. Important feed- saving features are the solid lower section and the slanted divider bars to a higher place.
Water Equipment
Many watering equipment system options are available. Dissimilar systems may be used throughout the year. If y'all are grazing animals, you may want portable water tanks to reduce the impact of cattle in ane location. In the winter, depending upon your climate, you may need heated units for utilise in pasture. There are many things to consider when selecting a system for use on your farm. The most important factor to sympathize your livestock' water needs and ensure that the current system can come across those requirements.
Headgate
The headgate is the about of import office of the entire working facility. It should be sturdy, safe, easy to operate, and work smoothly and quietly. Headgates come in four basic types; self catching, scissors-stanchion, positive-control and fully opening stanchion. The self-catching headgate closes automatically due to the move of the animal. The scissors-stanchion type has biparting halves that pivot at the lesser. The positive-control type locks firmly around the animal'south cervix. The fully opening stanchion consists of two biparting halves that work like a pair of sliding doors. The self-catching, scissor-stanchion and the fully opening stanchion are available with either straight or curved stanchion bars. The straight-bar stanchion is extremely safe and will rarely choke an animal. The disadvantage is animals can move their heads upwards and down unless a nose bar is used. The curved-bar stanchion offers more control of the animal's head but is more likely to choke the animal than the direct-bar type. Both types are safer than the positive-control headgate. No affair which blazon of headgate is selected, proper adjustment for the type of cattle beingness worked is necessary to prevent injury to the animals.
Holding Chute
The holding chute is secured to the caput gate and located immediately backside information technology. The belongings chute should generally non be any wider than 26 inches merely should be adjustable in gild to compensate for different-size animals. The sides should be solid so that animals are non able to expect out and be scared past their surroundings.
Working Chute
The working chute connects the belongings chute with the holding pen. Information technology should be long enough to concord five to half dozen animals at a time.
Crowding Pen
The crowding pen is located at the back of the working chute. Size should be about 150 square anxiety. This area will hold five or half dozen head of cattle.
Holding Pens
Property pens should mesh conveniently with the rest of the facility. Each holding pen should provide approximately 20 foursquare feet of space per animal.
Scales
Scales are optional depending on your size operation only can be useful in weighing cattle. The scales should be located and then cattle tin can be easily moved on and off. Exercise not locate scales in highly trafficked areas.
Loading Chute
The loading chute may be optional if a trailer is used to transport animals. The loading chute should be located directly off the crowding pen.
Conclusion
While improving your ability to handle cattle efficiently and safely does price both time and money, it is an investment that provides an excellent an often immediate return. A number of options are available if you lot want to install a new facility or improve an existing one, enabling you to improve your facility so that it meets your needs without exceeding your resources.
Note: Equally a dominion, all ages of cattle can stay on pasture during the warm weather months. Pastured or grass fed beefiness is a growing trend with New England beefiness producers and the consumer's need for this product is increasing.
Note: A ane or two-sided structure with a roof can provide shelter to cattle during periods of intense cold. Structures should be built with the open sides facing the south or eastward (depending upon prevailing winds) to maximize furnishings of solar radiation during the winter.
Note: Cattle on boilerplate can eat i gallon of h2o per 100 pounds alive weight per day.
Resources
Regime of Saskatchewan Agriculture. "Beefiness Cattle Housing and Feedlot Facilities". 2008.
Source: https://ag.umass.edu/crops-dairy-livestock-equine/fact-sheets/beef-cattle-housing-equipment
0 Response to "Beef Cattle Facilities Feet Beef Cattle Facilities Rooming"
Post a Comment